
We are often asked questions like: “What’s the difference between a gasket, a seal, and an O-ring?” It’s a great question, and understanding these distinctions will ensure you choose the right sealing solution for your application.
At first glance they may appear to be the same, but when it comes to keeping fluids, gases, or contaminants where they belong, gaskets, seals, and O-rings., each has a unique role in maintaining the integrity of the systems they protect. Choosing the right one is critical for performance, safety, and efficiency.
In this article, we will break down the differences between gaskets, seals, and O-rings, and explain when to use each.
Regardless of the type of seal, material selection for gaskets, seals, and O-rings is always based on operating criteria such as temperature range, pressure, chemical compatibility, regulatory approval, and mechanical performance. A common approach that ensures whether your application requires a gasket, seal or O-ring it will deliver reliable sealing in its intended environment.
What is a Gasket?
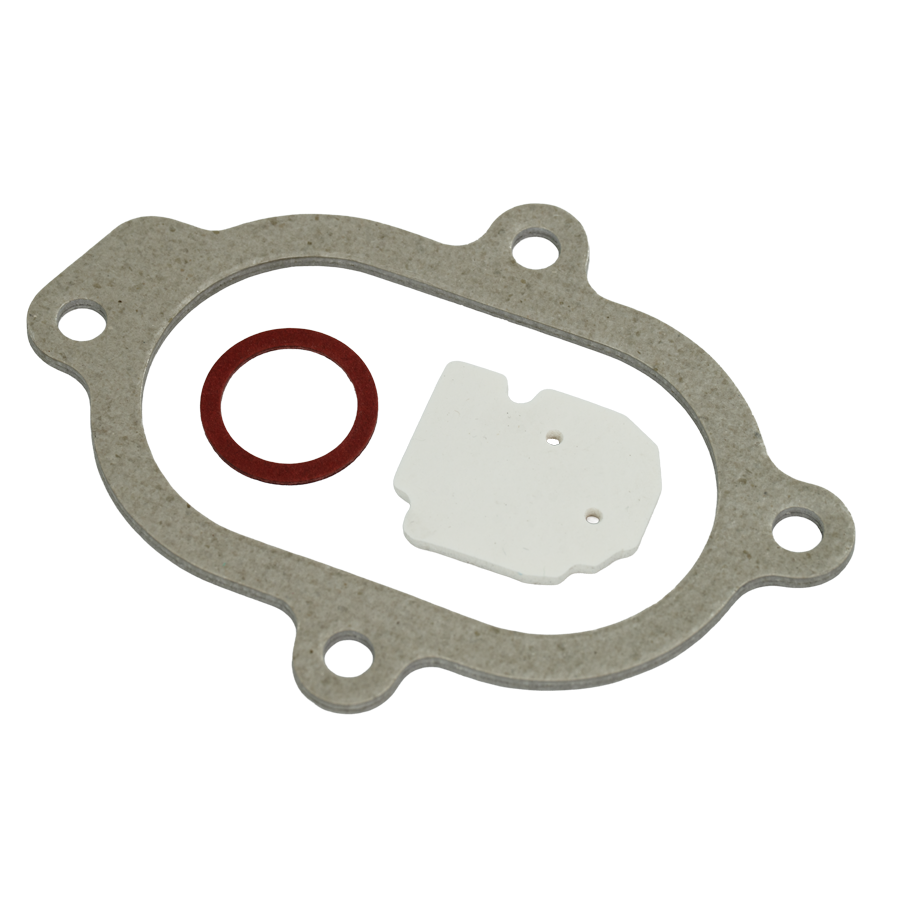
A gasket is a flat or shaped component that sits between two mating surfaces to primarily prevent leaks, the ingress of any foreign body, and in certain applications reducing noise transfer. Typically compressed between flanges, housings, or covers, gaskets create a tight seal under pressure.
- Materials: Can be manufactured in a wide range of materials including, Rubber (EPDM, Viton®, Nitrile), compressed fibre, graphite, PTFE, metal, or composite laminates.
- Common Uses: Flanged pipe joints, pumps, heat exchangers, automotive applications, HVAC systems, electrical enclosures etc.
- Key Benefits:
- Excellent for irregular or uneven surfaces
- Wide choice of materials for chemical, temperature, or fire resistance
- Can be cut or moulded to suit complex shapes
Short description: Gaskets seal static joints between rigid surfaces.
What is a Seal?
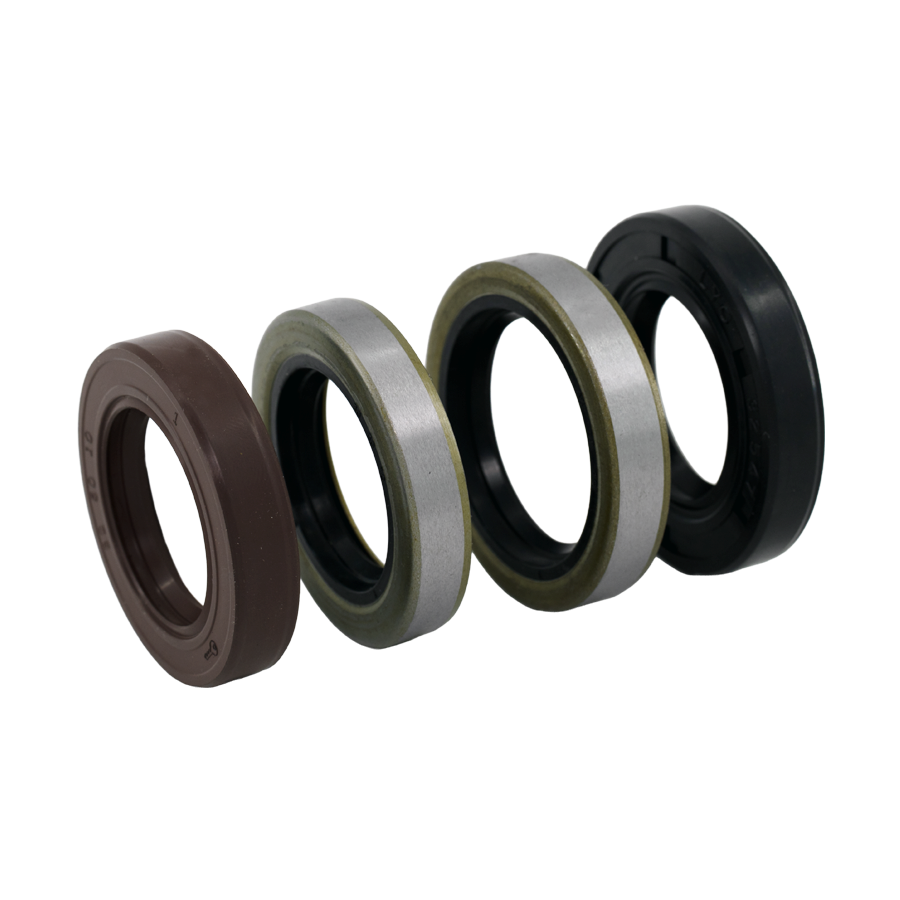

A seal can be used as a generic term to include any component designed to prevent leakage or ingress of fluids, dust, or gases.
However, unlike gaskets, seals are often employed to deal with dynamic applications where there is relative motion at the intersection between moving components, such as rotating shafts or piston rings.
- Types of Seals: Oil seals, mechanical seals, rotary shaft seals, lip seals.
- Materials: Elastomers, PTFE, polyurethane, sometimes bonded to metal for rigidity.
- Common Uses: Pumps, gearboxes, bearings, engines, and hydraulic systems.
- Key Benefits:
- Withstands movement and pressure
- Protects against contamination (dust, dirt, water)
- Extends equipment life
Short description: Seals can cover static applications, but primarily cover dynamic applications, providing a seal between moving parts.
What is an O-Ring?
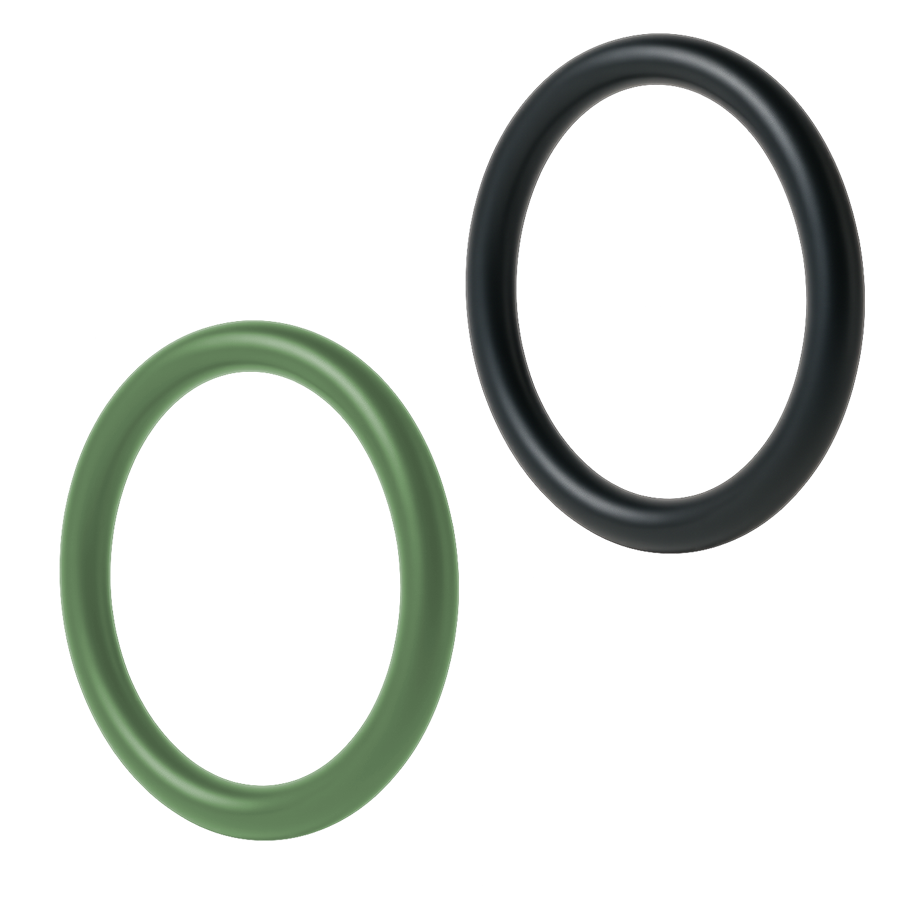
An O-ring is one of the simplest and most commonly used sealing components. It is a doughnut-shaped ring of elastomer that sits in a groove and compresses between two surfaces.
- Materials: Nitrile (NBR), EPDM, FKM/Viton®, Silicone, PTFE.
- Common Uses: Hydraulic fittings, pneumatic systems, plumbing, automotive, aerospace, food and pharma.
- Key Benefits:
- Simple, low-cost design
- Works in static and dynamic environments
- Standard sizes readily available (BS, AS, ISO ranges)
Short description: O-rings are compact, versatile, and ideal for both static and moving applications.
Gasket vs Seal vs O-Ring — Key Differences
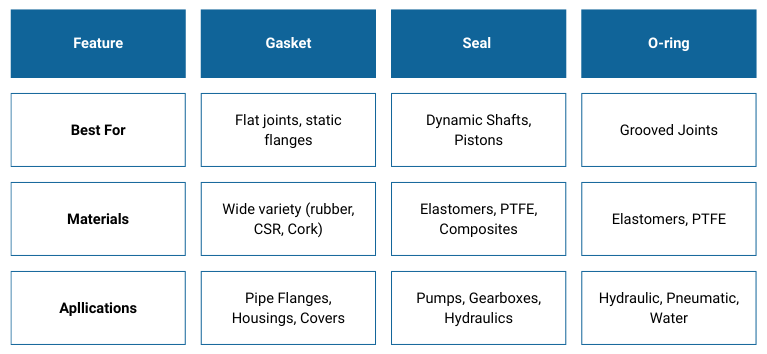
A quick guide to choosing the right option.
- Use a gasket if you are sealing two static, flat surfaces such as flanges.
- Choose a seal if your application involves movement (shafts, rotating parts).
- Select an O-ring when you need a simple, versatile, and low-cost solution for either static or dynamic sealing.
To make sure you make the right choice contact our team
